You are here
Targeting a Silent Killer: Dysautonomia After Spinal Cord Injury
Speakers
Abstract
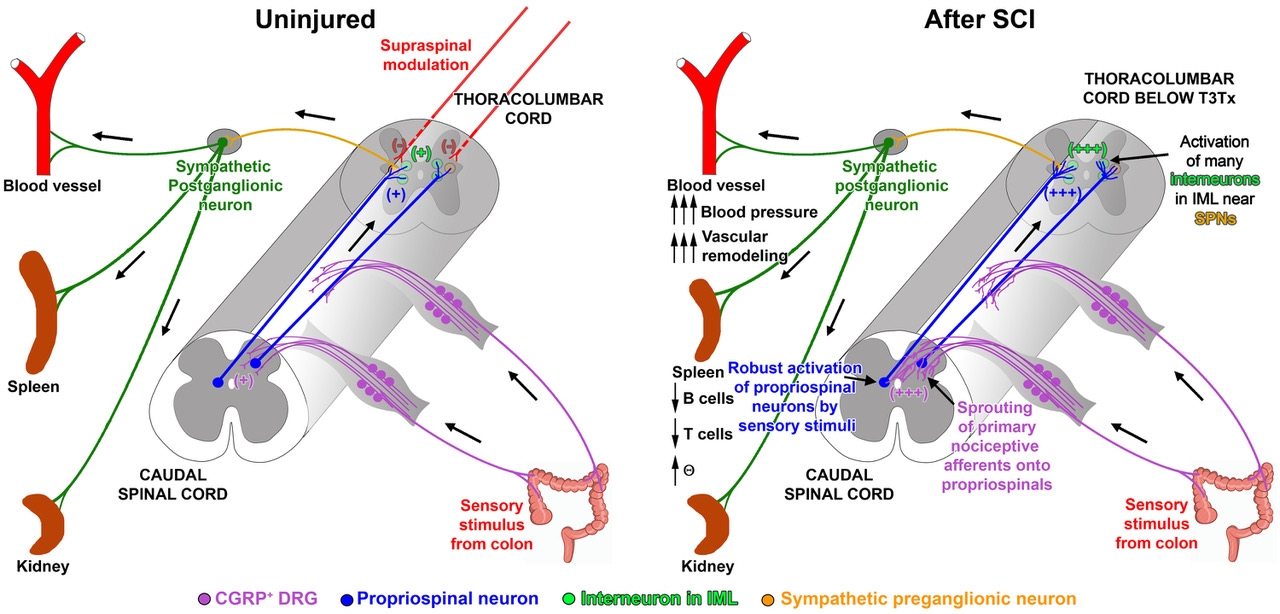
While not often appreciated, SCI affects normal functioning of multiple physiological systems. One major reason thought to underlie these issues is SCI-induced dysregulation of the sympathetic nervous system that results in significant, potentially life-threatening pathological changes of multiple organ systems in up to 70%-90% of people who have sustained a high SCI (above thoracic level 6). This is because the SCI interrupts modulatory control from the brain to neurons within the spinal sympathetic circuit in thoracolumbar spinal cord, allowing these neurons to become more responsive to intraspinal input. Also, injury induces maladaptive plasticity of the spinal sympathetic circuit below the SCI. Collectively, these contribute to the development of sympathetic hyperreflexia. The exaggerated sympathetic output detrimentally affects effector organs, such as the vasculature and the spleen, resulting in cardiovascular and immune dysfunction, respectively. Despite this, autonomic function after SCI is vastly understudied.
We will discuss these scientific questions:
- What mechanisms underlie neurogenic sympathetic hyperreflexia after SCI?
- How does SCI-induced sympathetic dysregulation affect effector organs?
- Can we restore descending input to the spinal sympathetic circuit?
- Is attenuating sympathetic hyperreflexia sufficient to prevent SCI-induced effector organ dysfunction?