You are here
Leveraging Synergistic Metabolic Therapies in Glioblastoma: PI3K Inhibitors and the Ketogenic Diet
Speakers
Abstract
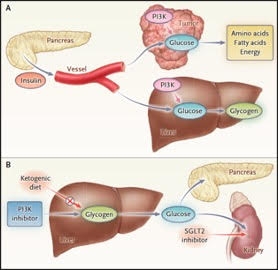
Glioblastoma (GBM) remains a poorly treatable disease with high mortality. Targeted therapies have gained interest in this disease, but efficacy is limited by therapeutic resistance, often because of tumor heterogeneity. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) inhibitors represent a strong drug class for GBM, but their use is associated with insulin feedback that reactivates the PI3K pathway and drives therapeutic resistance. Here, we target insulin feedback that is the primary mechanism of PI3K inhibitor-related therapeutic resistance in GBM using the ketogenic diet. We treated NOD scid gamma (NSG) mice containing patient-derived GBM xenografts with vehicle or BKM-120 on a regular or ketogenic diet to determine whether reducing insulin feedback increases BKM-120 efficacy. Mice with intracranial GBM xenografts survived longer and grew smaller and less glucose-avid tumors when treated with BKM-120 on the ketogenic diet than with BKM-120 or the ketogenic diet alone. We then modeled inflammation that can result from BKM-120-induced hyperglycemia. In vitro, BKM-120 and anti-hyperglycemic drugs reduced the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, and likewise, conditioned medium from these treated cells reduced oxidative stress in cultured cortical neurons that is caused by BKM-120 alone. Additionally, we re-analyzed results of a multi-institutional clinical trial testing the effects of BKM-120 in patients with recurrent GBM. We found that patients given BKM-120 exhibited higher serum glucose levels and that their glucose levels inversely correlated with progression-free survival. These findings indicate that BKM-120-mediated insulin feedback may have contributed to poor progression-free survival in this trial. Our results demonstrate that lowering glucose utilization and insulin feedback increases efficacy of PI3K inhibition and decreases features of neuro-inflammation. By using the ketogenic diet to reduce systemic glucose levels, this strategy may enhance efficacy and reduce morbidity of PI3K inhibitors in this population.