You are here
Gamma Oscillations: Mechanisms, Function and Human Diseases
Speakers
Abstract
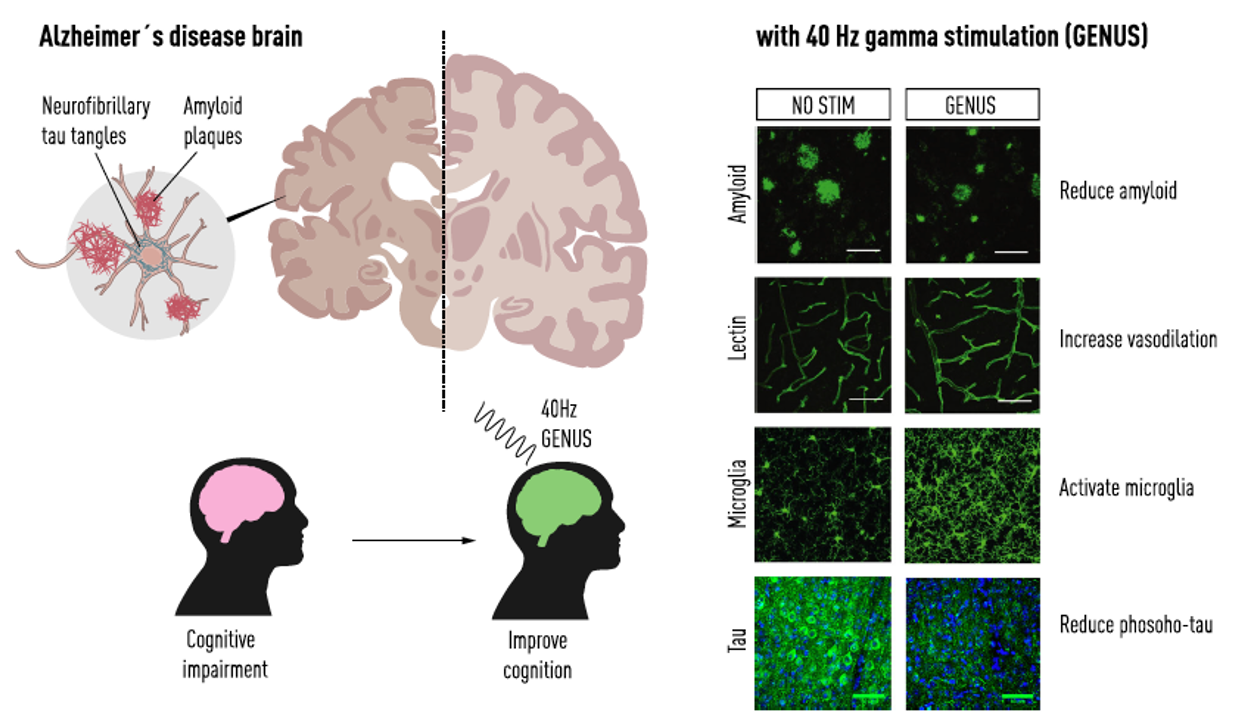
Rhythmic neural activity in the gamma range (30-80 Hz) is modulated during various aspects of cognitive function and is disrupted in several neurological conditions, including Alzheimer's disease (AD). It is well established that sensory stimuli can induce local network oscillations at specific frequencies in cortical regions. We have applied this approach, which we term Gamma ENtrainment Using Sensory stimuli (GENUS), using patterned light and sound stimulation at 40 Hz in AD model mice. We showed GENUS augmented gamma power in multiple brain regions. Moreover, daily application markedly reduced amyloid and tau pathology, attenuated degeneration of neurons and synapses, and improved cognitive function in multiple AD mouse models. In addition, GENUS induced morphological and gene expression changes of various cell types, including microglia and enhanced vasodilation. We extended these findings to evaluate the therapeutic potential of GENUS in human AD, and decipher the underlying cellular and physiological mechanisms of GENUS. In humans, GENUS promoted 40 Hz brain rhythms in cortical and subcortical brain regions, stabilized hippocampal volume in AD subjects, and maintained functional connectivity in the brain in pilot clinical studies. Our recent investigation has revealed that GENUS facilitates cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) influx and modifies meningeal lymphatic vasculature. Surprisingly, we found that depletion of microglia in AD model mice augmented the neuroprotective effects of GENUS. I will discuss our latest work aiming to decipher the mechanism underlying the effects of GENUS on ameliorating AD pathology and symptoms.